 23
23
Host cells are an important foundation of biological products, and many biological products, such as traditional vaccines, recombinant proteins, antibody drugs, cell therapy, gene therapy, mRNA-related, etc., are usually expressed and produced with Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO), African green monkey kidney cells (Vero), human embryonic kidney cells (HEK 293), Escherichia coli (E. coli), yeast, etc. as vectors.
Although the downstream purification process can remove residual impurities such as HCD, there may still be some HCD residues, and these residual exogenous DNA are easy to cause potential immunogenicity and safety issues, so HCD detection is one of the important quality detection indicators in the biologics production process.
Residual host cell DNA can have a variety of consequences when it enters the body:
The Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 Edition, General Chapter 3407 includes three methods for the determination of exogenous DNA residues: DNA probe hybridization, fluorescent staining, and quantitative PCR.
The exogenous DNA in the test sample was heated, denatured, and then adsorbed on a solid-phase membrane, and hybridized and refolded with specifically labeled single-stranded DNA to double-stranded DNA. After comparison with a known amount of positive DNA control, the amount of DNA is deeply reflected in color development, and the amount of exogenous DNA residue in the test sample can be determined.
A fluorescent signal is generated by application of a double-stranded DNA fluorescent dye that binds to double-stranded DNA to form a complex and is detected at a wavelength of 520 nm using a microplate reader, with fluorescence intensity proportional to the DNA concentration over a range of DNA concentrations. Based on the fluorescence intensity of the standard and test sample, the amount of residual DNA in the test sample is calculated.
After the reaction starts, the host cell DNA is denatured and melted into a single strand, the probe is preferentially annealed with the template strand, and the primer is then annealed to the template for strand extension, and the amplification enzyme exerts 5′-3′ exonuclease activity during the extension process, and the probe will be excised from the 5′ end one base by one when encountering the probe, and the fluorophore will be separated from the quencher to form a free fluorescent signal, which will be detected by the fluorescence detection system. A DNA standard of known concentration was used to construct a standard curve and the amount of exogenous DNA residue in the test sample was determined.
Quantitative PCR is the only standard method for the determination of exogenous DNA residues in biological products recommended by the new USP in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, and the only method recommended in the new USP for the detection of host residual DNA in biological products.
Characteristics of the method:
Features:
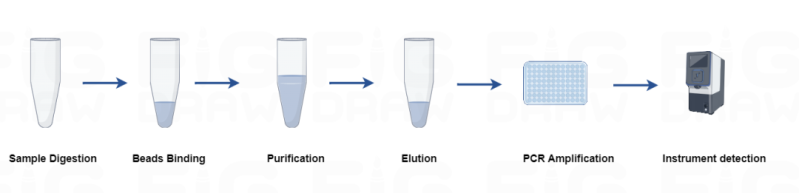
Hanhai New Enzyme has upgraded its host residual DNA detection products, covering multiple cell types such as CHO, E. coli, Vero, HEK293, Pichia pastoris, and mycoplasma. The primer and probe sequences of the kit are from the pharmacopoeia, so you don’t need to do a full set of validation experiments, just need to confirm the method. Developed based on a quantitative PCR method, LODs can reach 0.003 pg/μL with no cross-reactivity with other DNA, reducing false positives in the assay reaction. Strict production management system, batch-to-batch difference controllable CV<10%. Provide a complete set of solutions for manual extraction and automatic instrument extraction</b40>, which can quickly complete the detection within 2 hours and ensure the accuracy of quantitative detection.
Performance data
The standard products are calibrated by the national standard products
The standards in the CHO HCD kit were calibrated using the national CHO DNA standard, and the standard from different manufacturers was detected with the same kit, and the deviation of the measured value of the new enzyme standard was less than 5%.
The primer probe sequences for HCDs of CHO, Vero, E. coli, and yeast are from pharmacopoeia

Sensitivity, specificity, repeatability, precision
The test results of real samples are consistent
The finished product of the extraction reagent is assembled and used directly, without the need to prepare reagents separately, and the whole set is stored stably at room temperature. Fully automated instrument extraction with pre-packaged kits for flexible on-demand access.
References
[1] Technical Guidelines for Pharmaceutical Research and Evaluation of In Vivo Gene Therapy Products (Trial), Center for Drug Evaluation, National Medical Products Administration, May 2022
[2] Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (2020 edition).
[3] Yan Luyao, Zhang Jiayou, Yang Xiaoming. Research Progress on the Detection of Residual DNA from Host Cells in Biological Products[J]. Int J Biologics, 2021, 44(3): 170-174

