An Overall IVT Solution Based on HZYMES Raw Materials
During the development of the IVT process, high yield and high integrity of the product are the basic quality indicators that are first concerned. High yield is closely related to production cost, and high integrity is the most basic indicator of product quality.
T7 RNA polymerase, as the most important raw material in IVT translation, plays a decisive role in the quality of mRNA. Hzymes can provide a full set of materials for mRNA synthesis and a variety of T7 RNA polymerase mutants based on five technical platforms: enzyme gene resource mining, enzyme directed evolution, enzyme artificial intelligence design, enzyme large-scale manufacturing, and application technology research and development of enzyme catalytic systems. Based on in-depth research on different templates, different mutants, and IVT systems, it has screened and established its own IVT Buffer library to meet various production needs and application scenarios of customers.
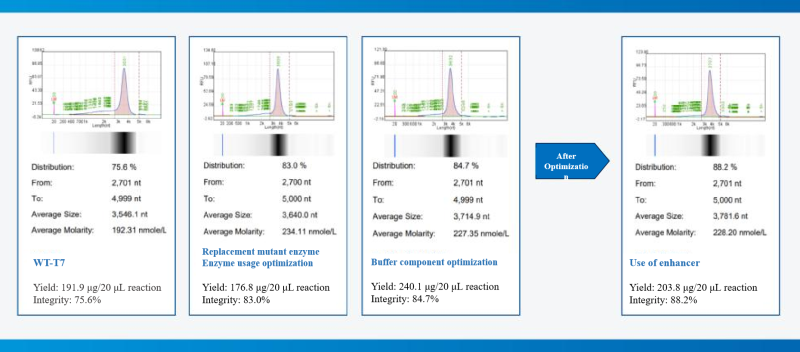
Case 1: Based on the T7 RNA polymerase mutant (HBP000330) and buffer library, help customers develop the IVT system to increase yield and purity.
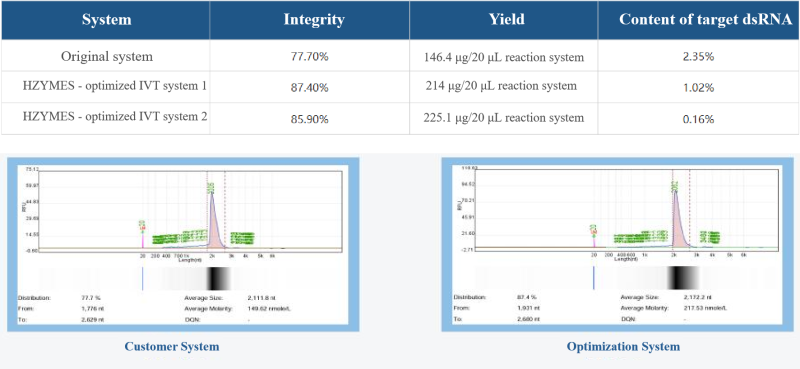
Case 2: Based on the T7 RNA polymerase low dsRNA mutant (HBP000340) and high-temperature resistant mutant (HBP000350), help customers develop the IVT system to reduce side reactions and the content of dsRNA in the final product.
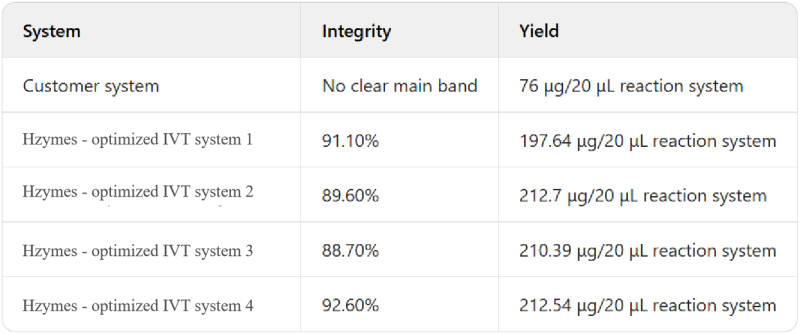
Case 3: Based on the T7 RNA polymerase mutant (HBP000330) and buffer library, help customers develop the IVT system for the production of extremely short fragments below 300nt.
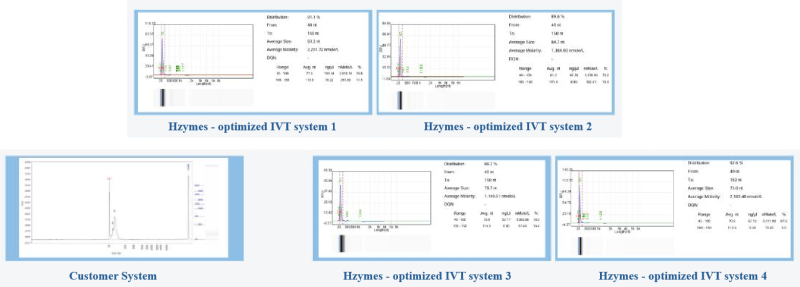
Case 4: Based on the T7 RNA polymerase mutant (HBP000330) and buffer library, help customers develop the IVT system for the production of ultra-long fragments and improve purity.
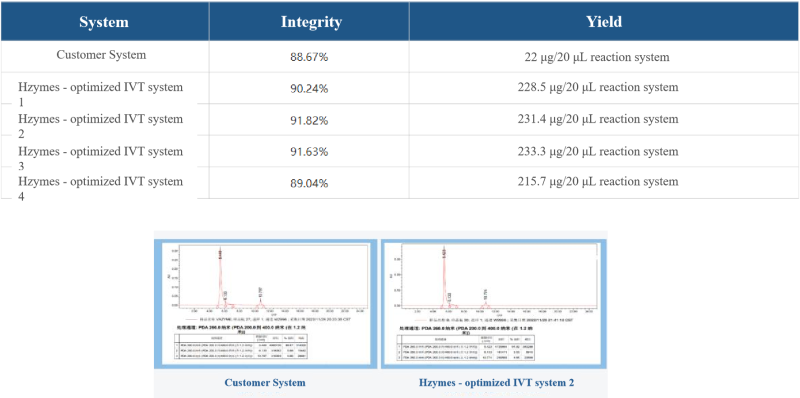
Case 5: Based on the T7 RNA polymerase mutant (HBP000330) and buffer library, help customers develop the IVT system for low-temperature IVT to improve the integrity of ultra-long fragment RNA.
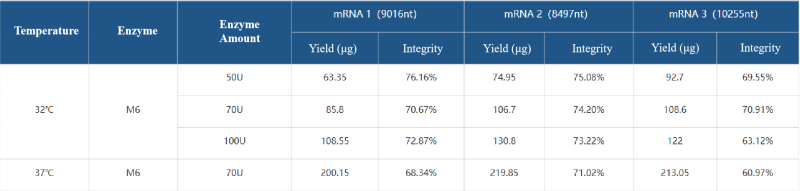
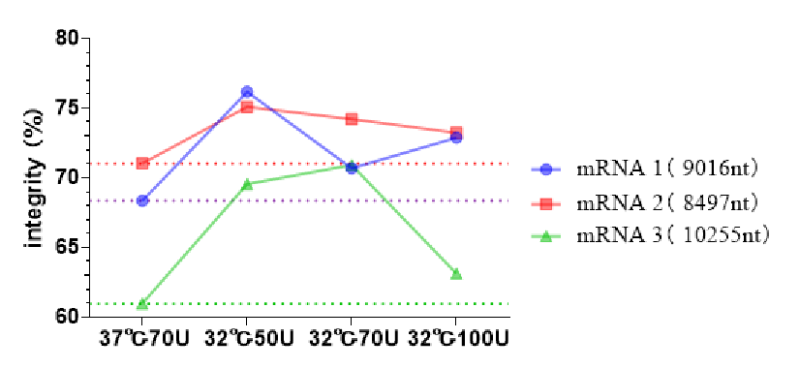
Low-temperature IVT mRNA synthesis.
LNP Process Development Service
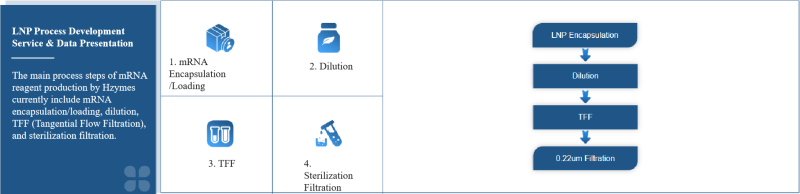
The basis of the encapsulation/loading process is the design and development of the delivery system. Only a well-designed delivery system can enable mRNA molecules to avoid degradation by RNA enzymes after entering the human body, be effectively delivered to the target site, cross the cell membrane, and be released intracellularly. Hzymes adopts the currently mainstream lipid nanoparticle delivery system.
The key to the preparation of mRNA-LNP encapsulation, in addition to the lipid composition formula, is the control of the process, that is, how to control the contact and interaction process between mRNA and lipid components to form a stable, uniform, and high-yield mRNA-LNP complex. Hzymes also adopts the current mainstream microfluidic mixing technology. Since mRNA is soluble in acidic aqueous phase and liposomes are soluble in ethanol, high pressure is used to make the mRNA solution and the liposome solution form two jets that collide and mix. The strong turbulence makes the components fully mixed. At the same time, the ethanol phase is diluted, the pH of the solution changes, the liposomes precipitate to form lipid nanoparticles and form an encapsulation complex with mRNA.
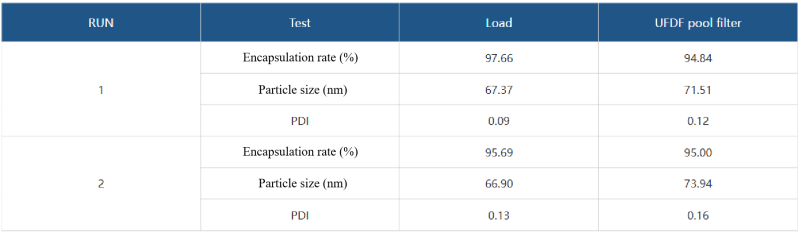
After mRNA encapsulation, purification is required to remove unencapsulated/loaded mRNA, free polymer or lipid materials, and adjust the final complex concentration, replace the solvent buffer system, and adjust the pH value. This step is usually achieved by tangential flow filtration. The mRNA-LNP complex is retained, and impurities and solvents are washed and filtered. Taking 4000nt mRNA as an example, after encapsulation, it is diluted 20 times and tangential flow filtration is carried out using a hollow fiber column. The following process data is for reference.
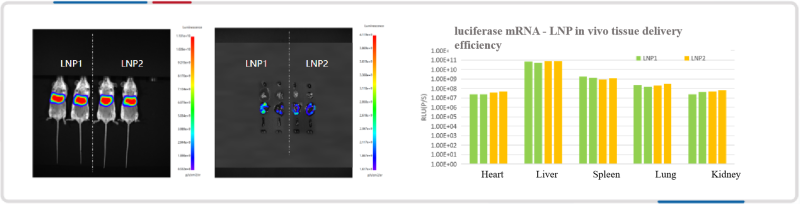
Firefly luciferase mRNA-LNP was delivered into mice, and the data showed that mRNA-LNP efficiently targeted the liver and spleen in vivo.
Purification Process Development
Purification process development and data display.
In the field of mRNA, in addition to designing and optimizing the sequence of mRNA and developing efficient and safe delivery vectors, developing a simple, fast, large-scale, and cost-effective mRNA preparation process is also one of the most important innovations in mRNA technology. In the production process of mRNA, purification after IVT is very important for the safety and effectiveness of the final mRNA product, because the content of impurities will affect the translation efficiency of mRNA and change the immunogenicity. Therefore, impurities need to be removed. Related impurities include residual substrates, dsRNA, abnormal mRNA, DNA templates, protease residues, etc. Commonly used purification methods include ultrafiltration, chromatography, precipitation, etc.
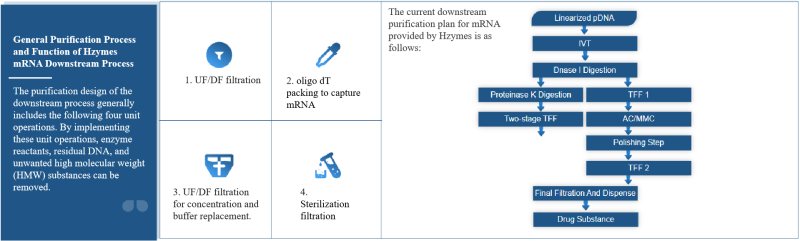
The general purification process and function of the mRNA downstream process of Hzymes New Enzyme.
The purification design of the downstream process generally includes the following four-unit operations. By implementing these unit operations, enzyme reactants, residual DNA, and unwanted high molecular weight (HMW) substances can be removed.
- The first step is UF/DF filtration. Start from receiving the IVT reaction product, then install the UF/DF filter, rinse with nuclease-free water, and balance with buffer. Then concentrate the product to the target volume, diafilter and replace it into the buffer, and finally recover the product by cleaning the UF/DF assembly. The purpose of this operation is to reduce impurities such as RNA polymerase, DNA template, NTPs, capping enzyme and reagents, inhibitors, etc., and replace the buffer system.
- The second step is to use oligo dT packing to capture mRNA or use multimodal nucleobase sphere chromatography. The former uses oligo dT (poly thymidine) ligand (18 – 25 bp thymine deoxynucleotide) and the polyadenylic acid (PolyA tail) at the 3′ end of mRNA to form a stable hybrid through hydrogen bonds to capture mRNA. Purpose: Remove impurities lacking the PolyA tail, such as free nucleotides, short-chain transcripts, enzymes, etc. The latter is an mRNA flow-through packing, and the flow-through and rinse fractions are collected as a single fraction and enter the next step. The purpose of this step is to remove contaminants of IVT reaction components.
- The third step is UF/DF filtration for concentration and buffer replacement. Replace the target product into the final formulation buffer and perform a top wash on the UF/DF assembly to recover the product.
- The fourth and final step is 0.2 µm sterilization filtration. Then fill the closed drug substrate stock solution into a sterile container. It should be noted that any tubing, chromatography, or filtration components that cannot be detected and confirmed to be nuclease-free should be maintained with 0.5M NaOH for at least 1 hour under environmental conditions, and then rinsed with nuclease-free water and an appropriate buffer for the next unit operation.
Finally, these purified mRNA drug substrate stock solutions can be further encapsulated into LNP.
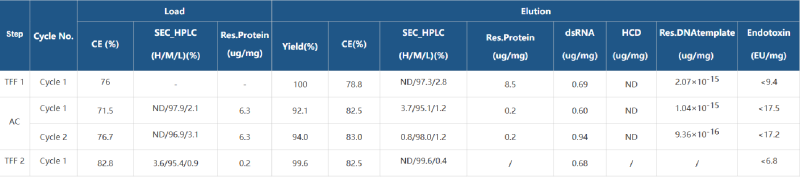
Taking 4000nt mRNA as an example, the relevant data of the purification process are as follows.











Please first Loginlater ~