Hzymes Leads the Formulation of Three Group Standards for Biological Products
Recently, the Key Laboratory for Vaccine and Biological Product Quality Monitoring and Evaluation under the National Medical Products Administration, in collaboration with Wuhan Hzymes Biotechnology Co., Ltd., has jointly formulated three group standards:
- 1. Quantitative Detection of dsRNA Impurities in mRNA Vaccines and Drugs via ELISA Method
- 2. Detection of DNase Residue in Biological Products via Nucleic Acid Fluorescence Substrate Method
- 3. Detection of RNase Residue in Biological Products via Nucleic Acid Fluorescence Substrate Method

Source: China Association for Quality Promotion of Pharmaceutical and Food Enterprises
These standards provide detailed explanations for the quantitative detection of dsRNA, as well as the detection of DNase and RNase residues.
dsRNA Quantitative Detection Kit
During the preparation of mRNA, T7 RNA polymerase transcribes DNA, which simultaneously forms by-products of various lengths of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA). Exogenous dsRNA can be recognized by Toll-like receptors (TLR), Retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I), and Melanoma Differentiation-Associated Protein 5 (MDA5) in cells, activating signaling pathways that release cytokines such as TNF-α and IFN-γ, leading to inflammatory responses. On one hand, dsRNA can reduce mRNA translation efficiency through feedback regulation between the immune system and the translation system; on the other hand, it can create immune memory, reducing the drug's efficacy.
To monitor and control the residual amounts of key impurities in vaccines, it is necessary to strictly control the dsRNA content during mRNA production.
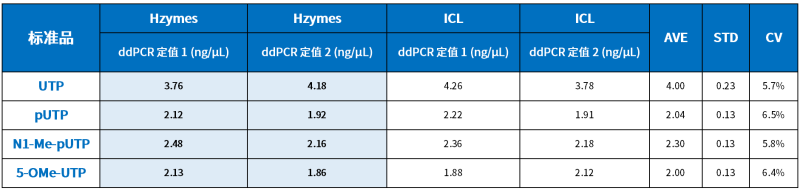
01 Precision – Quantification of dsRNA Reference Standards
According to the national “Standard Substance Management Measures,” for first-class standard substances, absolute measurement methods or two or more accurate and reliable methods based on different principles should be used for quantification. When there is only one quantification method available, multiple laboratories should use the same accurate and reliable method for quantification.
Hzymes dsRNA reference standards are quantified using UV spectrophotometry and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR).
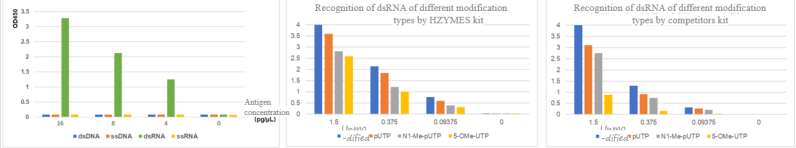
02 Specificity – Antibody Pair Specificity
Antibody pairs with strong affinity and specificity for dsRNA are selected and produced in-house. These antibody pairs specifically recognize dsRNA and do not recognize ssRNA, ssDNA, or dsDNA.
Since there is a difference in recognition specificity of different UTP-modified dsRNAs, the kit is equipped with four types of dsRNA reference standards with different modifications to ensure specificity in measurement.
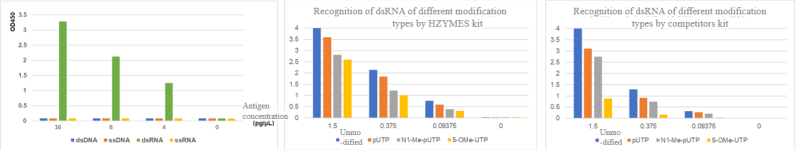
03 Comprehensive Coverage – Recognition of Short, Medium, and long dsRNA Fragments by Antibody Pairs
The formation of dsRNA is primarily based on random short fragments forming double strands with the original RNA molecule by reverse complementary pairing, and 3′ end RNA extending further to form a hairpin structure by pairing with the original RNA molecule. The length distribution of dsRNA cannot be accurately analyzed at present.
Hzymes kit exhibits minimal differences in the recognition of short, medium, and long dsRNA fragments, better reflecting the true levels of dsRNA in samples and ensuring accurate measurement
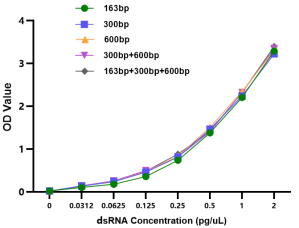
04 Uniformity – Consistent Recognition of dsRNA with Different Lengths and Sequences
The antibody pairs consistently recognize dsRNA of different lengths and sequences, as well as mixed standard substances with different lengths.
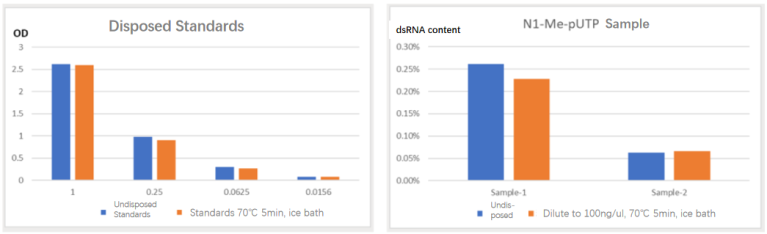
05 Structure Doesn't Affect Measurement – Heating and Denaturation of Reference Standards and Samples Do Not Affect Measurement
The ELISA method relies on the specific recognition of dsRNA by antibody pairs, and the secondary structure of mRNA does not alter the recognition of dsRNA by antibody pairs.
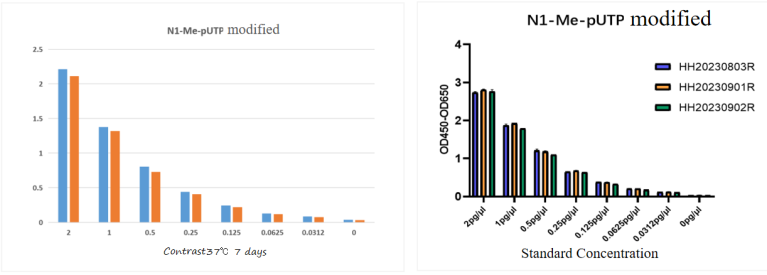
06 Stability – Heat Acceleration at 37°C, Batch Stability
Strict production management and quality control systems ensure that the kit remains stable after 7 days of heat acceleration at 37°C, with inter-batch variation (CV) less than 10%.
DNase/RNase Detection Kit
During the production of mRNA drugs, plasmids, and other biological products, there is a possibility of residual and contaminant DNase/RNase, including endogenous DNase/RNase present in biological samples, and exogenous DNase/RNase present in the environment, buffers, consumable surfaces, and raw materials. If residual DNase/RNase enters the human body with biological products, it may trigger high-intensity immunogenic reactions and pose serious safety risks. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately analyze and detect DNase/RNase residues in external materials, consumables, and environments to ensure they are controlled within safe limits.
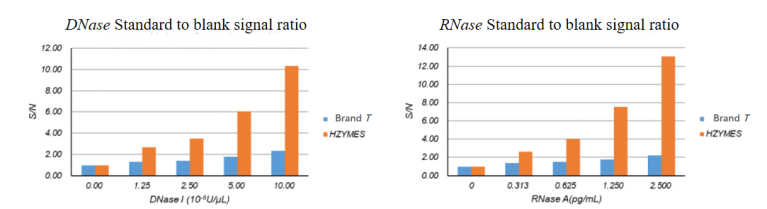
01 High Sensitivity – 8 Times Higher Sensitivity than Imported Brands
The standard for judgment is: if the ratio of detection signal to blank signal is greater than 2, it indicates contamination. The detection limit of DNase in imported brands is 1×10-5 U/μL, while the detection limit of Hzymes DNase is 1.25×10-6 U/μL. The detection limit of RNase in imported brands is 2.5 pg/mL, while the detection limit of Hzymes RNase is 0.3125 pg/mL.
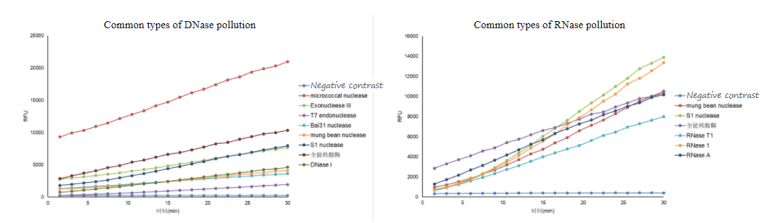
02 Comprehensive Detection – Detection of Multiple Types of Enzymes
The kit’s probes are designed with special sequences that can recognize multiple types of enzymes, meeting the detection needs of various scenarios and samples.
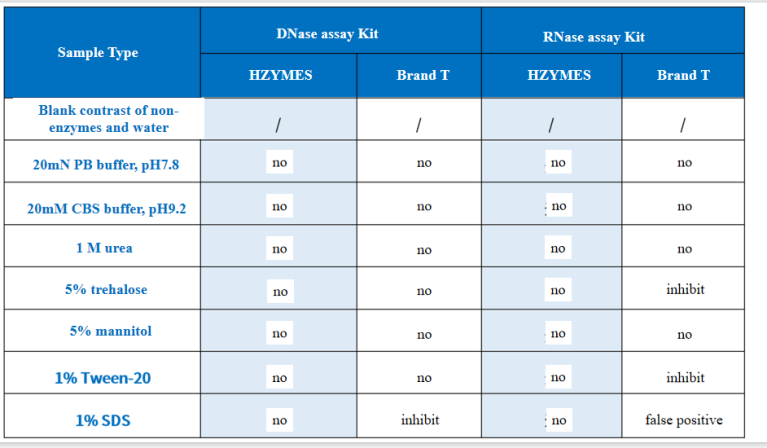
03 Reliability – Strong Anti-Interference Ability
Commonly used buffers or materials in test experiments do not interfere with the kit.
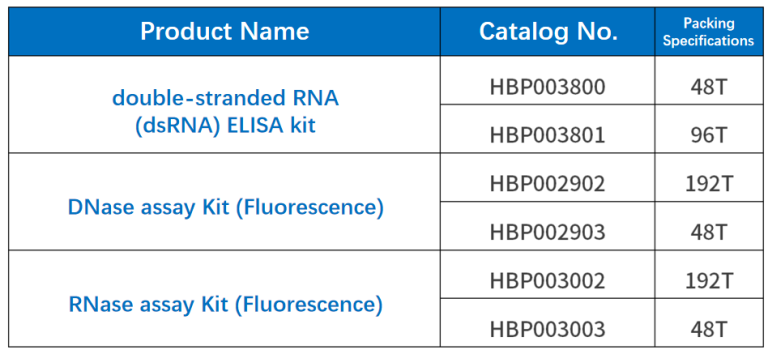
Product Information











Please first Loginlater ~